How does a fan motor circuit work?

The main principle of operation of a fan is the rotation of an energised coil by force in a magnetic field.
As the fan converts electrical energy into mechanical energy in order to turn the fan blades. At the same time, the operation of coil resistance will generate thermal energy, so that the surface of the electric fan will generally become hot after a certain length of operation.
The thermal energy is generated by kinetic energy, which can be shown in the circuit diagram. In order to see the operating process more clearly, CAD renderings have been designed to show the internal structure of the motor.
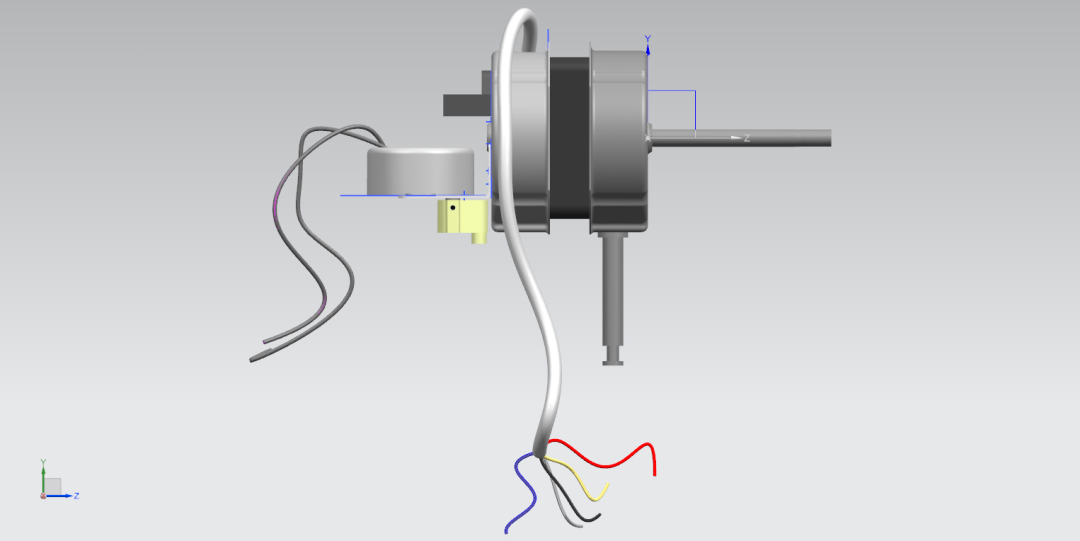
A circuit diagram is also drawn to illustrate the operation of the motor. The following are the circuit diagrams of the three types of fans:
I.
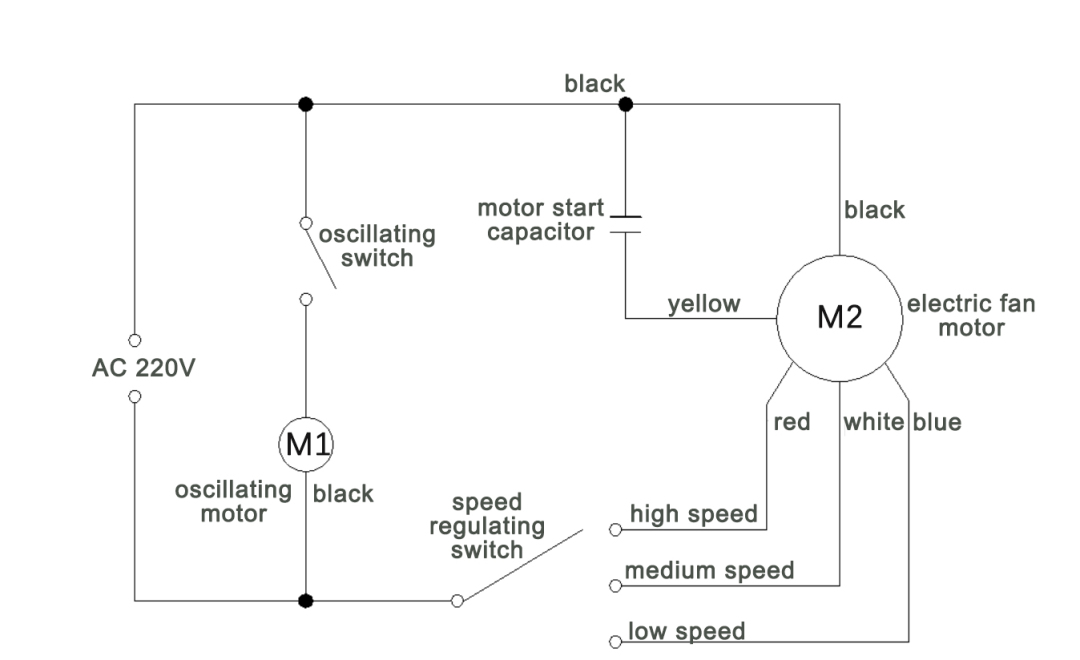
The circuit diagram above we can divide into three main parts. The first part is the 220V AC power circuit on the far left; the second part is the swing circuit in the middle; and the third part is the motor circuit on the far right.
The motor of the fan in the picture is a single-phase AC motor which has two internal windings, one called the running winding (main winding) and the other the starting winding (secondary winding). The starting circuit consists of a phase-splitting capacitor, which allows the main and secondary windings to be spatially separated by an electrical angle of 90°. The speed control
circuit is composed of a reactance speed switch connected in series, which changes the voltage of the motor by adjusting the size of the reactance to achieve speed control.
II.
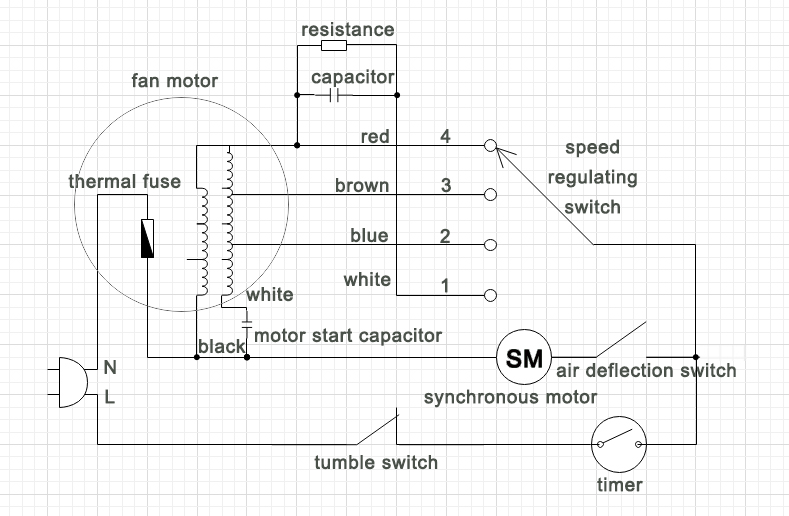
This working schematic can be seen at the tumble switch, which is a circuit diagram for a box fan.
The circuit of the box fan consists mainly of the speed switch, the air deflection switch, the tumble switch, the synchronous motor, the rotating blade motor and the timer connection. When the fan is in an upright position, the tumble switch is switched on and at this time turn on the timer switch, the speed switch is set to a gear and current flows through the motor to start running the fan. When the air guide switch is pressed, the synchronous motor is fed with AC current at both ends and starts to rotate, thus driving the wind deflector to guide the air. At this time the fan can deliver air and also control the wind direction.
III.
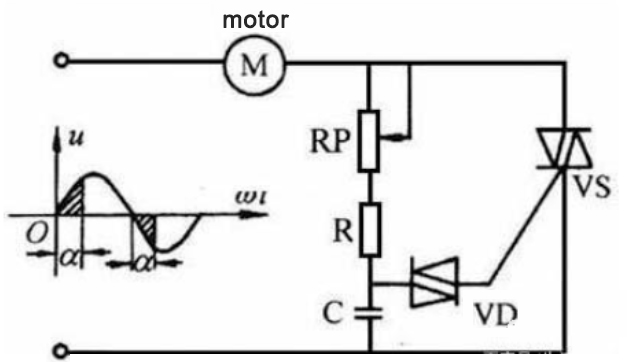
Stepless speed control generally uses a bidirectional thyristor as a switch for the fan motor.The principle is to use the controllable characteristics of the thyristor, by changing the control angle α of the thyristor, the output voltage of the thyristor is changed in order to regulate the motor speed. At the beginning of each half cycle of the supply voltage, the bi-directional thyristor VS is blocked, the supply voltage is charged to capacitor C through potentiometer RP and resistor R. When the charging voltage on capacitor C reaches the trigger voltage of the bi-directional trigger diode VD, VD conducts and C discharges to the control pole of VS through VD, causing VS to conduct and current to flow through the motor winding. By adjusting the resistance value of potentiometer RP, the charging time constant of capacitor C can be adjusted, which also adjusts the control angle α of the bidirectional thyristor VS. The larger the RP, the larger the control angle α, and the voltage on the load motor M becomes smaller and the speed slows down.
The above is the circuit working principle diagram for each component and each switch depicting the operational relationship and process.
If you are interested, welcome to contact us:
![]() WhatsApp: +86 13144118381
WhatsApp: +86 13144118381
![]() Email: operating@fsshining.com
Email: operating@fsshining.com
![]() Web: www.fsshining.com
Web: www.fsshining.com
Spain Retail Services: www.fswinstep.com
![]() Foshan Shining Electrical Appliance Co., Ltd.
Foshan Shining Electrical Appliance Co., Ltd.




